Under the null hypothesis, the population has mean ![]() and
standard deviation
and
standard deviation ![]() .
.
Using either the fact that the data are normal or the fact that the central limit
theorem applies, assume that the data are from a
Normal![]() distribution.
distribution.
With this assumption, if the null hypothesis is true, the sample mean
![]() will be normally distributed with the following parameters:
will be normally distributed with the following parameters:
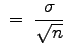
The strategy for testing the hypothesis is to consider the sample mean as a single observation
from this distribution, standardize it based on the assumption that its mean is ![]() and
its standard deviation is
and
its standard deviation is
![]() , and base our decision to accept or reject the null hypothesis on where the standardized value or
, and base our decision to accept or reject the null hypothesis on where the standardized value or ![]() -score falls on the standard normal bell curve.
-score falls on the standard normal bell curve.
We calculate the standardized or ![]() -score for the sample mean as:
-score for the sample mean as:
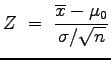
(This value is in cell B10)
The exact decision rule to accept or reject the null hypothesis depends on whether we want:
See the sections below for details on these three cases.